|
Education
Web
The Intimate Machine: Making Faces
One Step Further The six expressions cited above are the most basic and easiest to decipher as identified by Paul Ekman, one of the leaders in facial recognition. Can you think of other emotions and expressions that also present a characteristic appearance? If so, build them on...
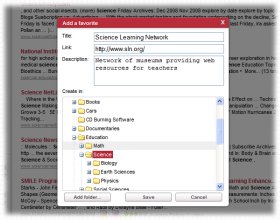
Polygon Capture: A Geometry Game
The purpose of this game is to motivate students to examine relationships among geometric properties. From the perspective of the Van Hiele model of geometry, the students move from recognition or description to analysis (Fuys 1988). Often, when asked to describe g...
The Flight: To Bounce or Not to Bounce
type of throw. Lead students in a discussion about vector components of motion using the analysis questions to guide the process. Data Table See Appendix E for Student Sheet...
Hominoid Cranium Comparison: The "Skulls" Lab
and after" photos of what they look like: ACRYLIC CALIPERS Before After 4. Carpet squares, foam pads, or similar table padding on which to set the casts for each student group or "Skull Station". TIME One to two 45-55 minute periods, depending on the amount of...
Math Forum: Learning About Buckyballs
Math Forum: Suzanne Alejandre: Buckyball Links Learning About Buckyballs Back to Student Activities || Suzanne's Math Lessons || Magic Squares || Tessellations Students wondering why we study about polyhedra can find one reason by looking through the information in the links to Buckybal...
Molecular Biology and Phylogeny
ASSESSABLE OBJECTIVES Students will.... 1. cite a valid example of independent confirmation. 2. explain why independent confirmation is important in science. 3. recognize what comparisons of molecular structure suggests about evolutionary relationships. MATERIALS...
definition maps, analogies, using the dictionary and other reference materials, using word parts, using morphemic analysis, using context clues ) word families: A collection of words that share common ortho- graphic rimes (e.g., thank, prank, dank). word recognition strategies:...
1
0
definition maps, analogies, using the dictionary and other reference materials, using word parts, using morphemic analysis, using context clues ) word families: A collection of words that share common ortho- graphic rimes (e.g., thank, prank, dank). word recognition strategies: Strategies for determining the pronun- ciation and meaning of words in print.
11
0
http://www.k12.wa.us/CurriculumInstruct/reading/pubdocs/ReadingEALR-GLE.pdf#page=11
www.k12.wa.us/CurriculumInstruct/reading/pubdocs/ReadingEALR-GLE.pdf#page...
GRADE LEVEL EXPECTATIONS 9 GLE 5 6 7 8 9/10 1.1.1 1.1.2 1.1.3 1.1.4 EALR 1: The student understands and uses different skills and strategies to read. <span class="highlight">Component</span> 1.1: Use word <span class="highlight">recognition</span> skills and strategies to read and comprehend text. EALR 1 “Phonemic Awareness and knowledge <span class="highlight">of</span> letters are the two best predictors <span class="highlight">of</span> how well children will learn to read.” n Linnea Ehri, Ph.D. National Reading Panel, City University <span class="highlight">of</span> New York
16
0
http://www.k12.wa.us/CurriculumInstruct/reading/pubdocs/ReadingEALR-GLE.pdf#page=16
www.k12.wa.us/CurriculumInstruct/reading/pubdocs/ReadingEALR-GLE.pdf#page...
pleasure reading vs. reading <span class="highlight">for</span> <span class="highlight">information</span>). Apply different reading rates to match text. square6 Adjust reading rate to match difficulty and type <span class="highlight">of</span> text and the purposes <span class="highlight">for</span> reading (e.g., skimming <span class="highlight">for</span> facts, scan- ning <span class="highlight">for</span> key words, and close/careful reading <span class="highlight">for</span> understanding new or complex ideas). Fluent readers focus attention on understanding what they read, rather than concentrating on decoding the words
20
0
http://www.k12.wa.us/CurriculumInstruct/reading/pubdocs/ReadingEALR-GLE.pdf#page=20
www.k12.wa.us/CurriculumInstruct/reading/pubdocs/ReadingEALR-GLE.pdf#page...
18 EALR <span class="highlight">COMPONENT</span> EALR 2 EALR 2: The student understands the meaning <span class="highlight">of</span> what is read. <span class="highlight">Component</span> 2.1: Demonstrate evidence <span class="highlight">of</span> reading comprehension. K 1 2 3 4 2.1.5 Understand how to infer/predict meaning. square6 Use pictures and culturally relevant text read aloud and/or during shared reading to predict what will happen next; support predictions using <span class="highlight">information</span> from the text. square6 Make inferences orally before, during, and after hearing a story using prior knowledge, story structure, and
29
0
http://www.k12.wa.us/CurriculumInstruct/reading/pubdocs/ReadingEALR-GLE.pdf#page=29
www.k12.wa.us/CurriculumInstruct/reading/pubdocs/ReadingEALR-GLE.pdf#page...
GRADE LEVEL EXPECTATIONS 27 EALR 2: The student understands the meaning <span class="highlight">of</span> what is read. <span class="highlight">Component</span> 2.3: Expand comprehension by analyzing, interpreting, and synthesizing <span class="highlight">information</span> and ideas in literary and informational text. EALR 2 GLE 5 6 7 8 9/10 2.3.1 Analyze informational/expository text and literary/narrative text <span class="highlight">for</span> similari- ties and differences and cause and effect relationships. W square6 Find similarities and differences within and between texts using text-based evi- dence (e.g., facts and
48
0
http://www.k12.wa.us/CurriculumInstruct/reading/pubdocs/ReadingEALR-GLE.pdf#page=48
www.k12.wa.us/CurriculumInstruct/reading/pubdocs/ReadingEALR-GLE.pdf#page...
46 EALR <span class="highlight">COMPONENT</span> EALR 4: The student sets goals and evaluates progress to improve reading. <span class="highlight">Component</span> 4.2: Develop interests and share reading experiences. EALR 4 GLE K 1 2 3 4 4.2.1 Understand how readers choose books. square6 Choose books and share with others with teacher guidance. Understand how readers choose books. square6 Identify favorite books and share reasons <span class="highlight">for</span> the choice with others. square6 Self-select books at an <span class="highlight">independent</span> level and an instructional level. Understand that readers have
53
0
http://www.k12.wa.us/CurriculumInstruct/reading/pubdocs/ReadingEALR-GLE.pdf#page=53
www.k12.wa.us/CurriculumInstruct/reading/pubdocs/ReadingEALR-GLE.pdf#page...
feelings. scan: To examine or read something quickly, but selectively, <span class="highlight">for</span> a purpose. scanning: Examining or read something quickly, but selectively, <span class="highlight">for</span> a purpose. schema: The accumulated knowl- <span class="highlight">edge</span> drawn from life experiences that a person has to help under- stand concepts, roles, emotions, and events. secondary sources: Sources <span class="highlight">of</span> <span class="highlight">information</span> that are derived from primary or original sources. segment: The act <span class="highlight">of</span> separating the sounds in a word in order to assist decoding or spelling. semantic mapping
54
0
http://www.k12.wa.us/CurriculumInstruct/reading/pubdocs/ReadingEALR-GLE.pdf#page=54
www.k12.wa.us/CurriculumInstruct/reading/pubdocs/ReadingEALR-GLE.pdf#page...
definition maps, analogies, using the dictionary and other reference materials, using word parts, using morphemic <span class="highlight">analysis</span>, using context clues ) word families: A collection <span class="highlight">of</span> words that share common ortho- graphic rimes (e.g., thank, prank, dank). word <span class="highlight">recognition</span> strategies: Strategies <span class="highlight">for</span> determining the pronun- ciation and meaning <span class="highlight">of</span> words in print.
Arizona Mathematics Standard Articulated by Grade Level The bulleted items within a performance objective indicate the specific content to be taught. Explanations and Examples Updated 1.19.09 Grade 5 Arizona Department of Education: Standards and Assessment Division 16 Approved 6.24.08 St...
1
0
Arizona Mathematics Standard Articulated by Grade Level The bulleted items within a performance objective indicate the specific content to be taught. Explanations and Examples Updated 1.19.09 Grade 5 Arizona Department of Education: Standards and Assessment Division 16 Approved 6.24.08 Strand 2: Data Analysis, Probability, and Discrete Mathematics Concept 4: Vertex-Edge Graphs Understand and apply vertex-edge graphs. In Grade 5, students continue to develop their
9
0
http://www.ade.state.az.us/standards/math/Articulated08/Gradeleveldocs/MathGrade5.pdf#page=9
www.ade.state.az.us/standards/math/Articulated08/Gradeleveldocs/MathGrade...
and the study <span class="highlight">of</span> graphs. This prepares students <span class="highlight">for</span> the study <span class="highlight">of</span> discrete functions as well as to make valid inferences, decisions, and arguments. Discrete mathematics is a branch <span class="highlight">of</span> mathematics that is widely used in business and industry. Combinatorics is the mathematics <span class="highlight">of</span> systematic counting. Vertex-<span class="highlight">edge</span> graphs are used to model and solve problems involving paths, networks, and relationships among a finite number <span class="highlight">of</span> objects. Concept 1: Data <span class="highlight">Analysis</span> (Statistics) Understand and apply data
16
0
http://www.ade.state.az.us/standards/math/Articulated08/Gradeleveldocs/MathGrade5.pdf#page=16
www.ade.state.az.us/standards/math/Articulated08/Gradeleveldocs/MathGrade...
Arizona Mathematics Standard Articulated by Grade Level The bulleted items within a performance objective indicate the specific content to be taught. Explanations and Examples Updated 1.19.09 Grade 5 Arizona Department <span class="highlight">of</span> Education: Standards and Assessment Division 16 Approved 6.24.08 Strand 2: Data <span class="highlight">Analysis</span>, Probability, and Discrete Mathematics Concept 4: Vertex-<span class="highlight">Edge</span> Graphs Understand and apply vertex-<span class="highlight">edge</span> graphs. In Grade 5, students continue to develop their
target for reading on own: Sixth grade, 750,000 words annually. increase word knowl- edge through systematic vocabulary development; determine the meaning of new words by apply- ing knowledge of word origins, word relation- ships, and context clues; verify the meaning ...
1
0
target for reading on own: Sixth grade, 750,000 words annually. increase word knowl- edge through systematic vocabulary development; determine the meaning of new words by apply- ing knowledge of word origins, word relation- ships, and context clues; verify the meaning of new words; and use those new words accurately across the subject areas . Find, understand, and use specific information in a variety of texts across the subject areas to perform a task . informAtionAL text: DemonstrAte generAL
1
0
http://www.ode.state.or.us/teachlearn/real/documents/el06.pdf#page=1
www.ode.state.or.us/teachlearn/real/documents/el06.pdf#page=1
target <span class="highlight">for</span> reading on own: Sixth grade, 750,000 words annually. increase word knowl- <span class="highlight">edge</span> through systematic vocabulary development; determine the meaning <span class="highlight">of</span> new words by apply- ing knowledge <span class="highlight">of</span> word origins, word relation- ships, and context clues; verify the meaning <span class="highlight">of</span> new words; and use those new words accurately across the subject areas . Find, understand, and use specific <span class="highlight">information</span> in a variety <span class="highlight">of</span> texts across the subject areas to perform a task . informAtionAL text: DemonstrAte generAL
Arizona Mathematics Standard Articulated by Grade Level The bulleted items within a performance objective indicate the specific content to be taught. Explanations and Examples Updated 1.19.09 Grade 7 Arizona Department of Education: Standards and Assessment Division 18 Approved 6.24.08...
1
0
Arizona Mathematics Standard Articulated by Grade Level The bulleted items within a performance objective indicate the specific content to be taught. Explanations and Examples Updated 1.19.09 Grade 7 Arizona Department of Education: Standards and Assessment Division 18 Approved 6.24.08 Strand 2: Data Analysis, Probability, and Discrete Mathematics Concept 4: Vertex-Edge Graphs Understand and apply vertex-edge graphs. In Grade 7, students use vertex-edge
10
0
http://www.ade.state.az.us/standards/math/Articulated08/Gradeleveldocs/MathGrade7.pdf#page=10
www.ade.state.az.us/standards/math/Articulated08/Gradeleveldocs/MathGrade...
counting, and the study <span class="highlight">of</span> graphs. This prepares students <span class="highlight">for</span> the study <span class="highlight">of</span> discrete functions as well as to make valid inferences, decisions, and arguments. Discrete mathematics is a branch <span class="highlight">of</span> mathematics that is widely used in business and industry. Combinatorics is the mathematics <span class="highlight">of</span> systematic counting. Vertex-<span class="highlight">edge</span> graphs are used to model and solve problems involving paths, networks, and relationships among a finite number <span class="highlight">of</span> objects. Concept 1: Data <span class="highlight">Analysis</span> (Statistics) Understand and apply data
18
0
http://www.ade.state.az.us/standards/math/Articulated08/Gradeleveldocs/MathGrade7.pdf#page=18
www.ade.state.az.us/standards/math/Articulated08/Gradeleveldocs/MathGrade...
Arizona Mathematics Standard Articulated by Grade Level The bulleted items within a performance objective indicate the specific content to be taught. Explanations and Examples Updated 1.19.09 Grade 7 Arizona Department <span class="highlight">of</span> Education: Standards and Assessment Division 18 Approved 6.24.08 Strand 2: Data <span class="highlight">Analysis</span>, Probability, and Discrete Mathematics Concept 4: Vertex-<span class="highlight">Edge</span> Graphs Understand and apply vertex-<span class="highlight">edge</span> graphs. In Grade 7, students use vertex-<span class="highlight">edge</span>
|