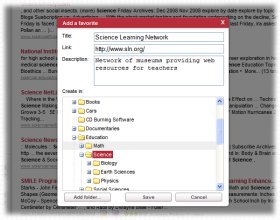
|
Education
Web
Viewing 1-1 of 1 total results
Science Podcast: Accurate Automatic Face Recognition; Complete Synthesis of a Genome; Unde...
facial recognition to 100% by using what they call an "averaged" face. In the future, it could mean a new kind of photo for your passport. I spoke to Jenkins from his office at the University of Glasgow. Interviewee - Rob Jenkins As you know, there&rsqu...
1
0
facial recognition to 100% by using what they call an "averaged" face. In the future, it could mean a new kind of photo for your passport. I spoke to Jenkins from his office at the University of Glasgow. Interviewee - Rob Jenkins As you know, there’s increasing interest in security applications and security infrastructure and biometrics in general. The problem is, a lot of the face recognition systems that are out there simply don’t work at anything like the level that people think they do. So for some
1
0
http://www.sciencemag.org/cgi/data/319/5862/499b/DC1/1#page=7
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/data/319/5862/499b/DC1/1#page=7
facial <span class="highlight">recognition</span> to 100% by using what they call an "averaged" <span class="highlight">face</span>. In the future, it could mean a new kind <span class="highlight">of</span> photo <span class="highlight">for</span> your passport. I spoke to Jenkins from his office at the University <span class="highlight">of</span> Glasgow. Interviewee - Rob Jenkins As you know, there’s increasing interest in security applications and security infrastructure and biometrics in general. The problem is, a lot <span class="highlight">of</span> the <span class="highlight">face</span> <span class="highlight">recognition</span> systems that are out there simply don’t work at anything like the level that people think they do. So <span class="highlight">for</span> some
2
0
http://www.sciencemag.org/cgi/data/319/5862/499b/DC1/1#page=8
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/data/319/5862/499b/DC1/1#page=8
we realized that we could exploit this setup to try to get at the performance level <span class="highlight">of</span> that <span class="highlight">face</span> <span class="highlight">recognition</span> system on images <span class="highlight">of</span> real world variability. So these are images that contain all the variability in lighting and so on that we are used to dealing with in the real world. But it’s exactly that <span class="highlight">information</span> that usually trips up the automatic systems. And so the logic behind this was that if the system is performing well, and we feed it a photograph <span class="highlight">of</span> Bill Clinton, it should tell us that the closest
|